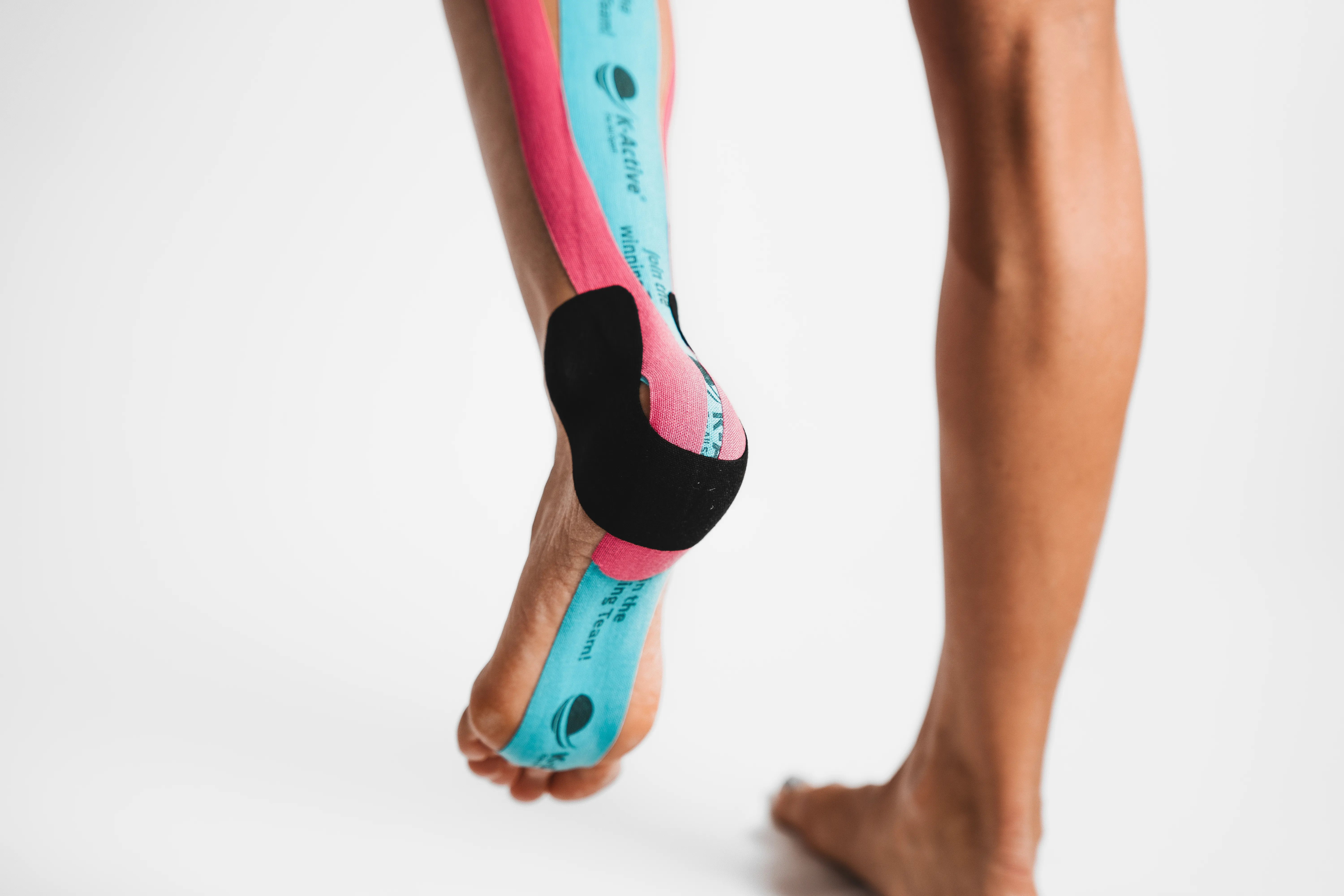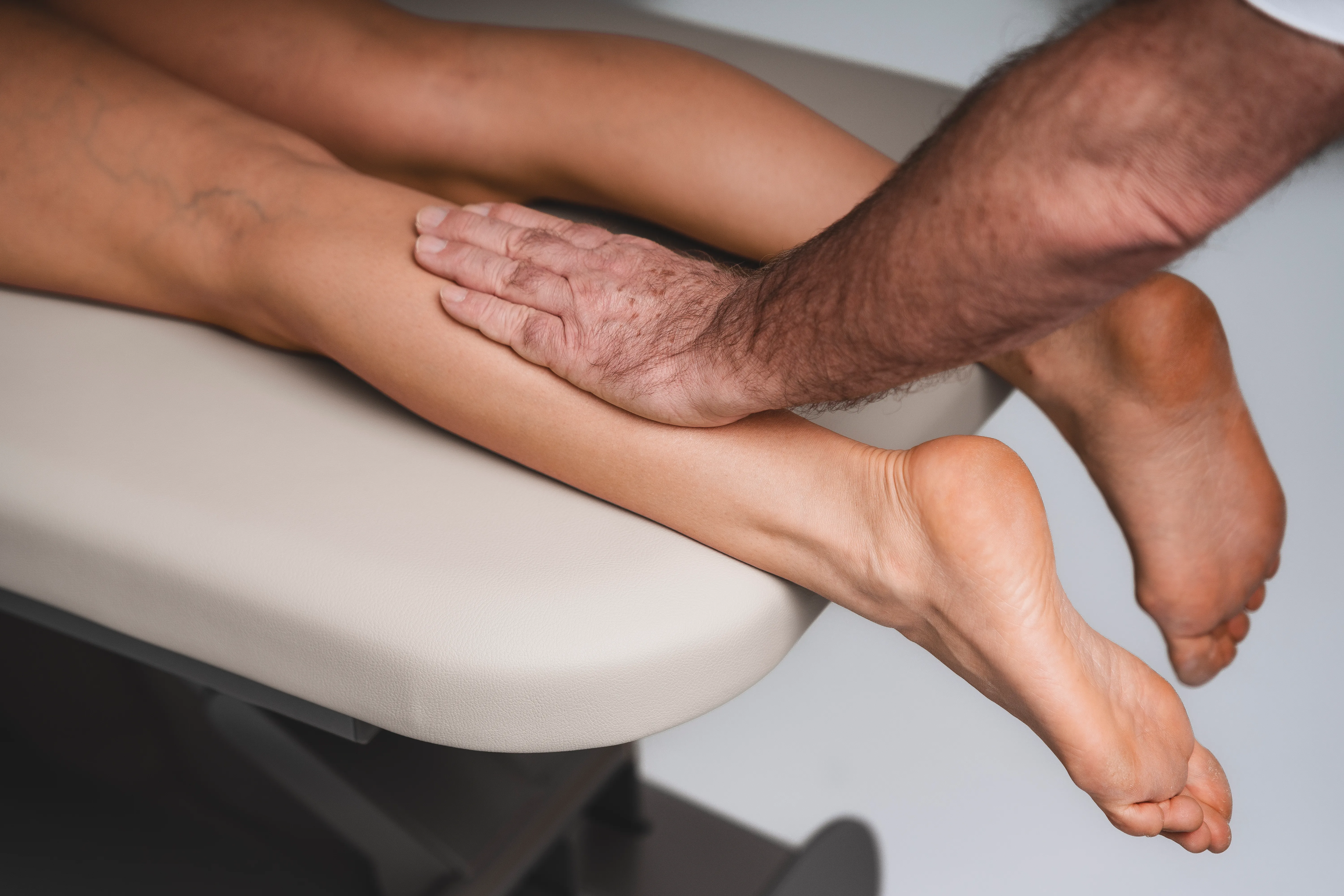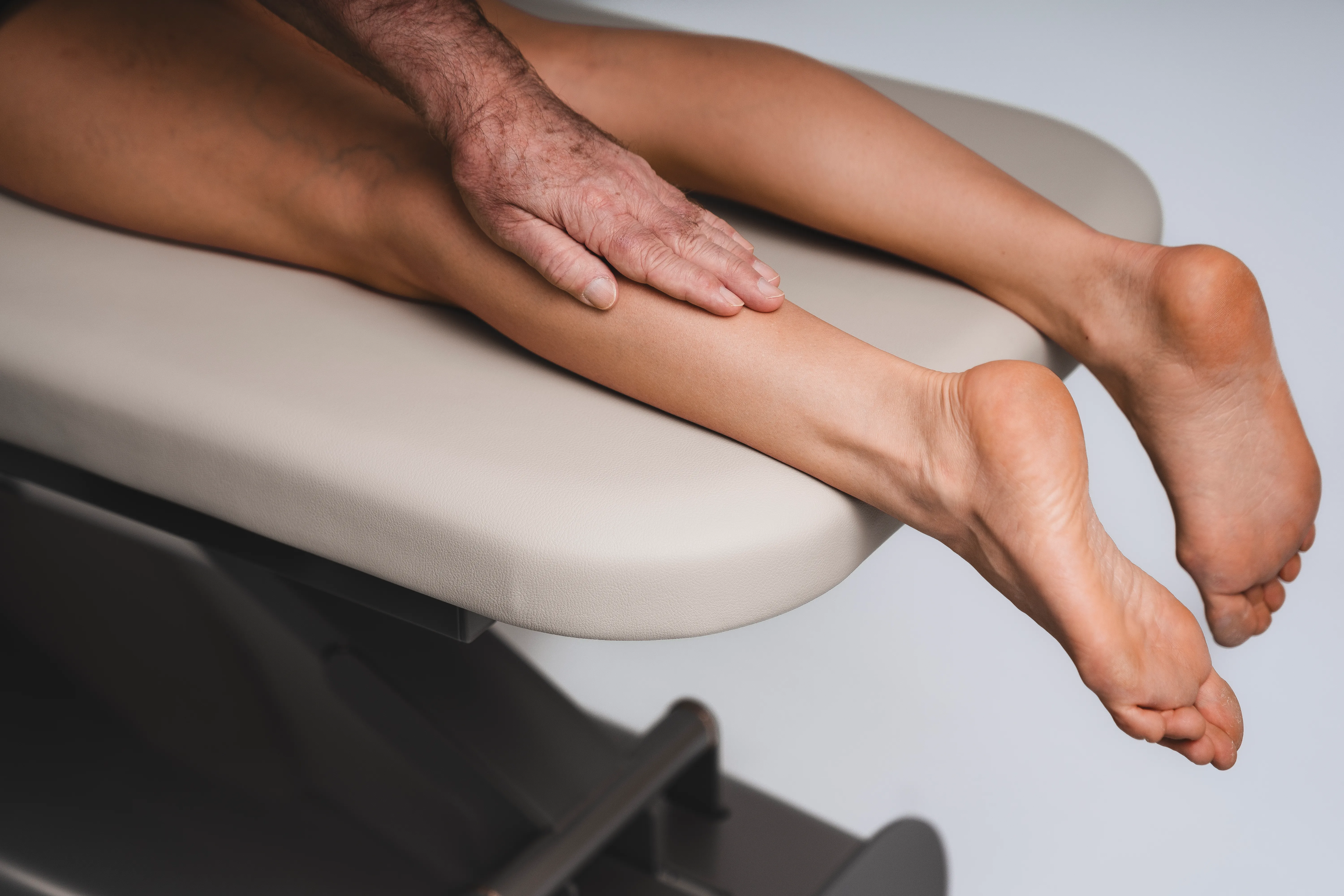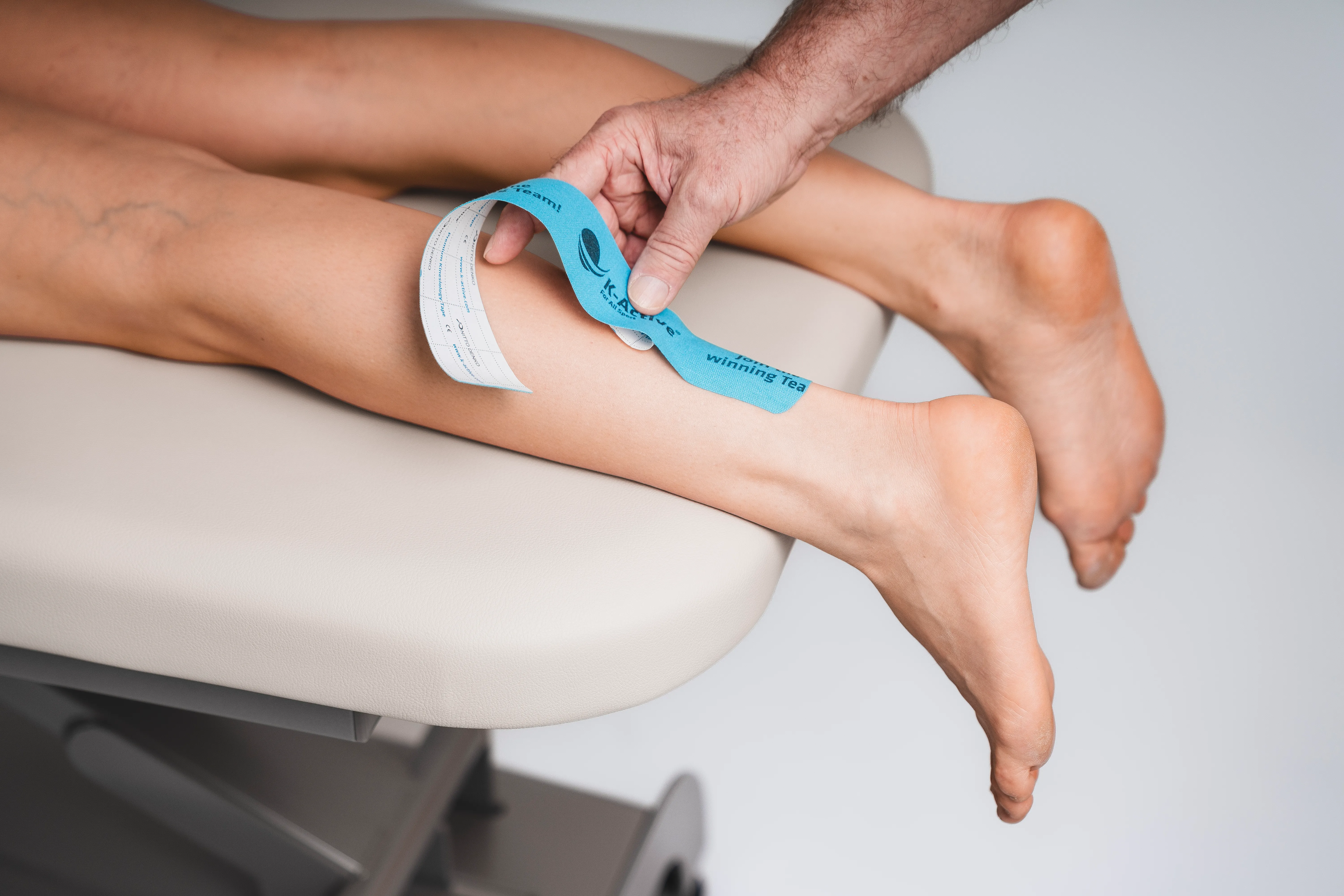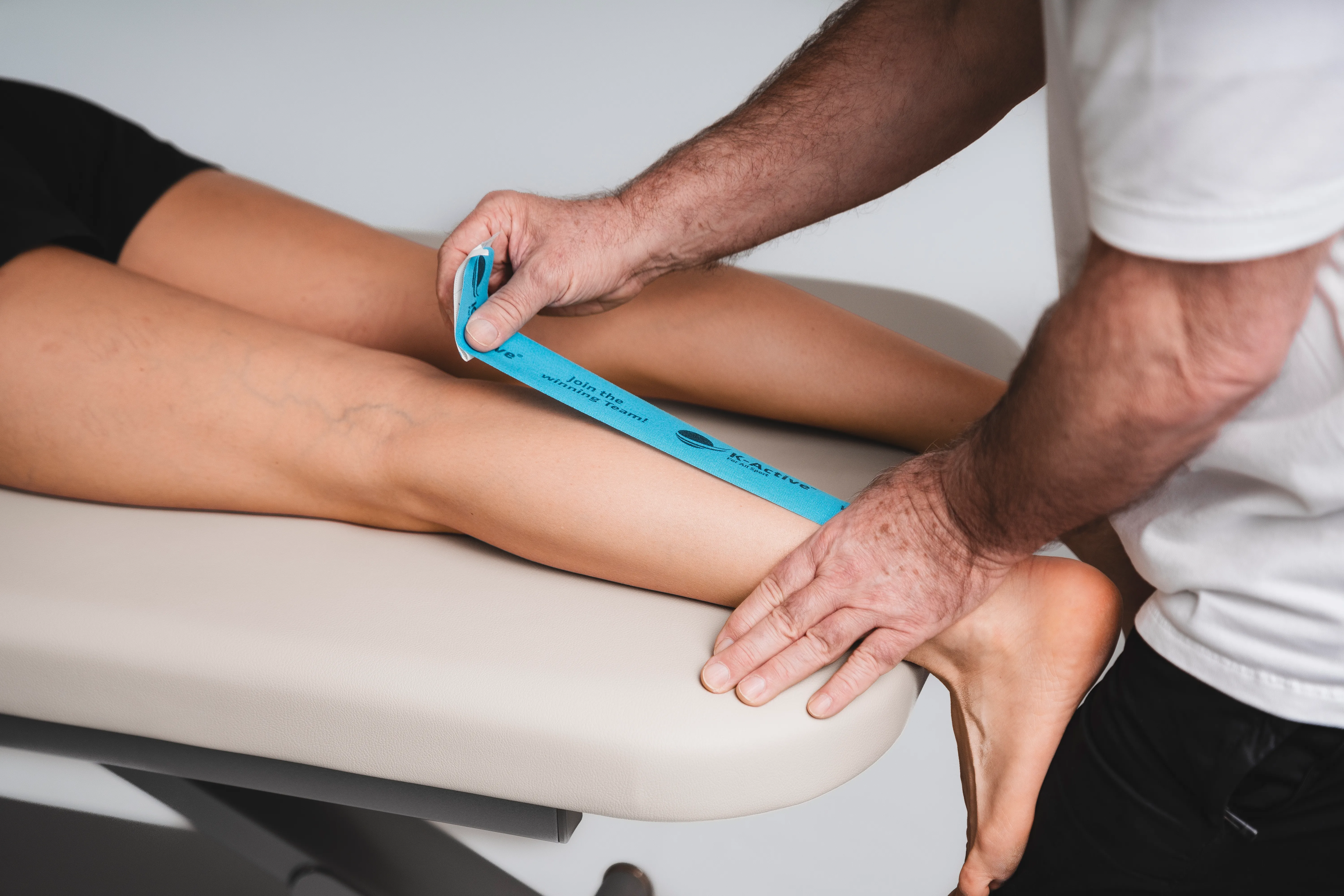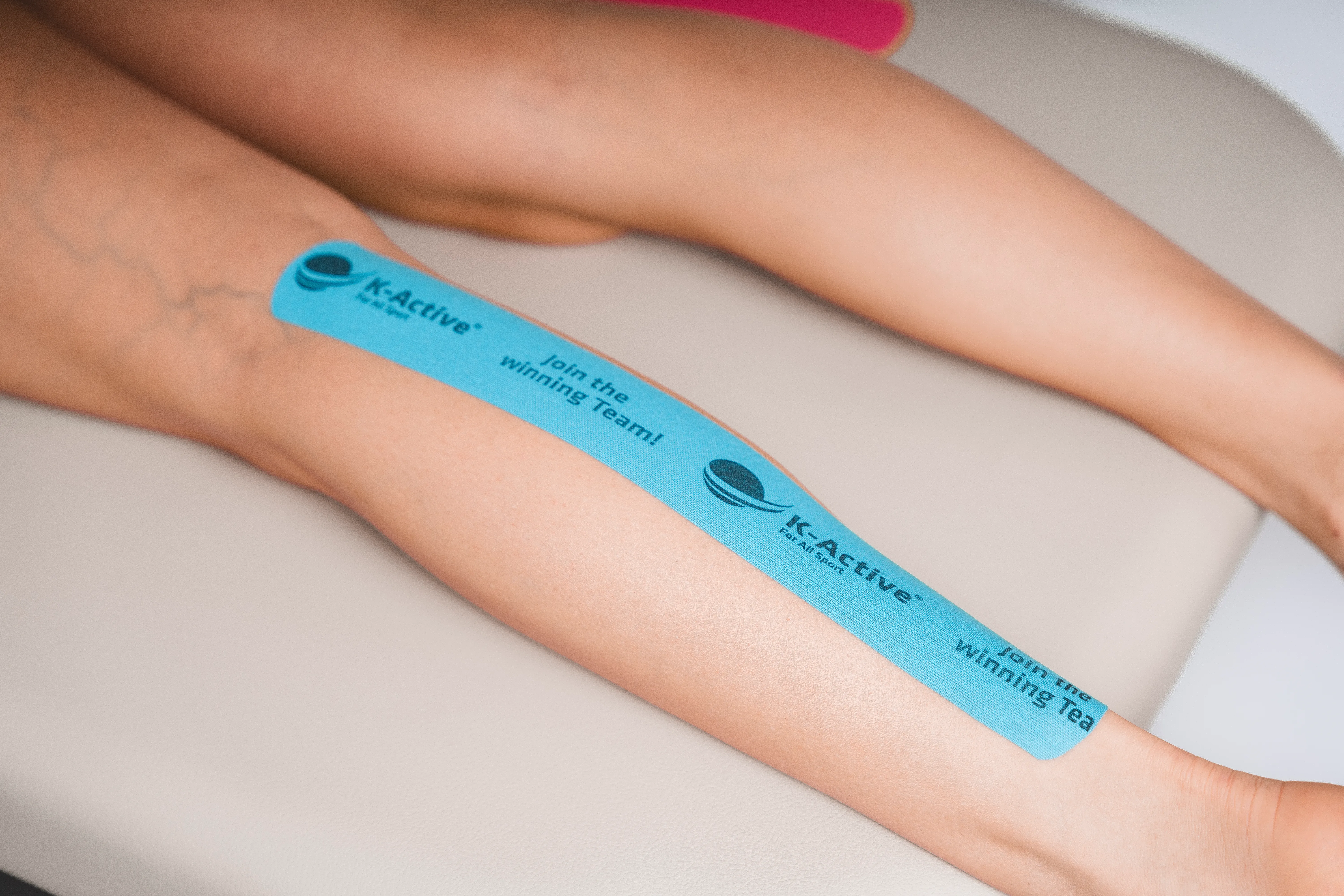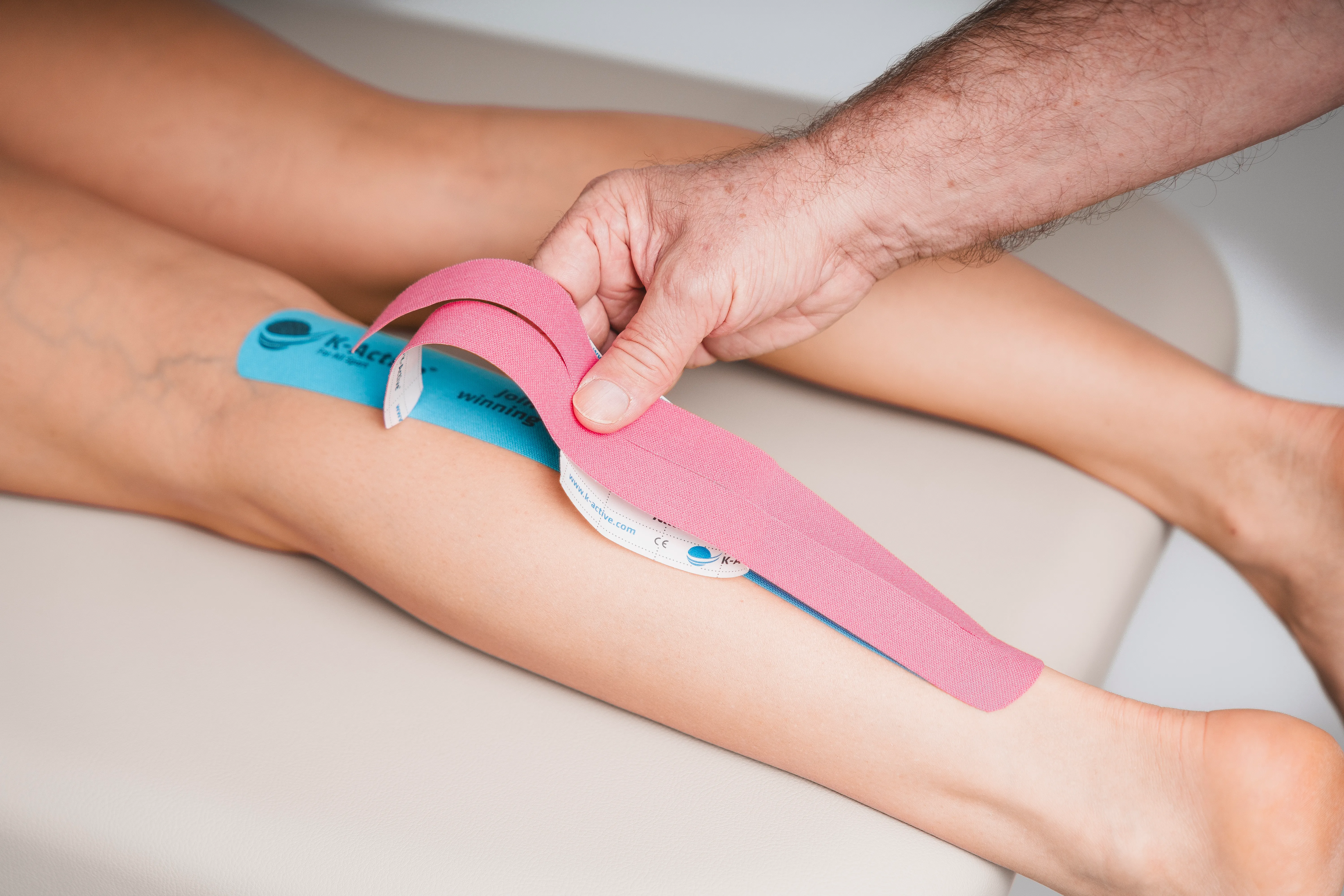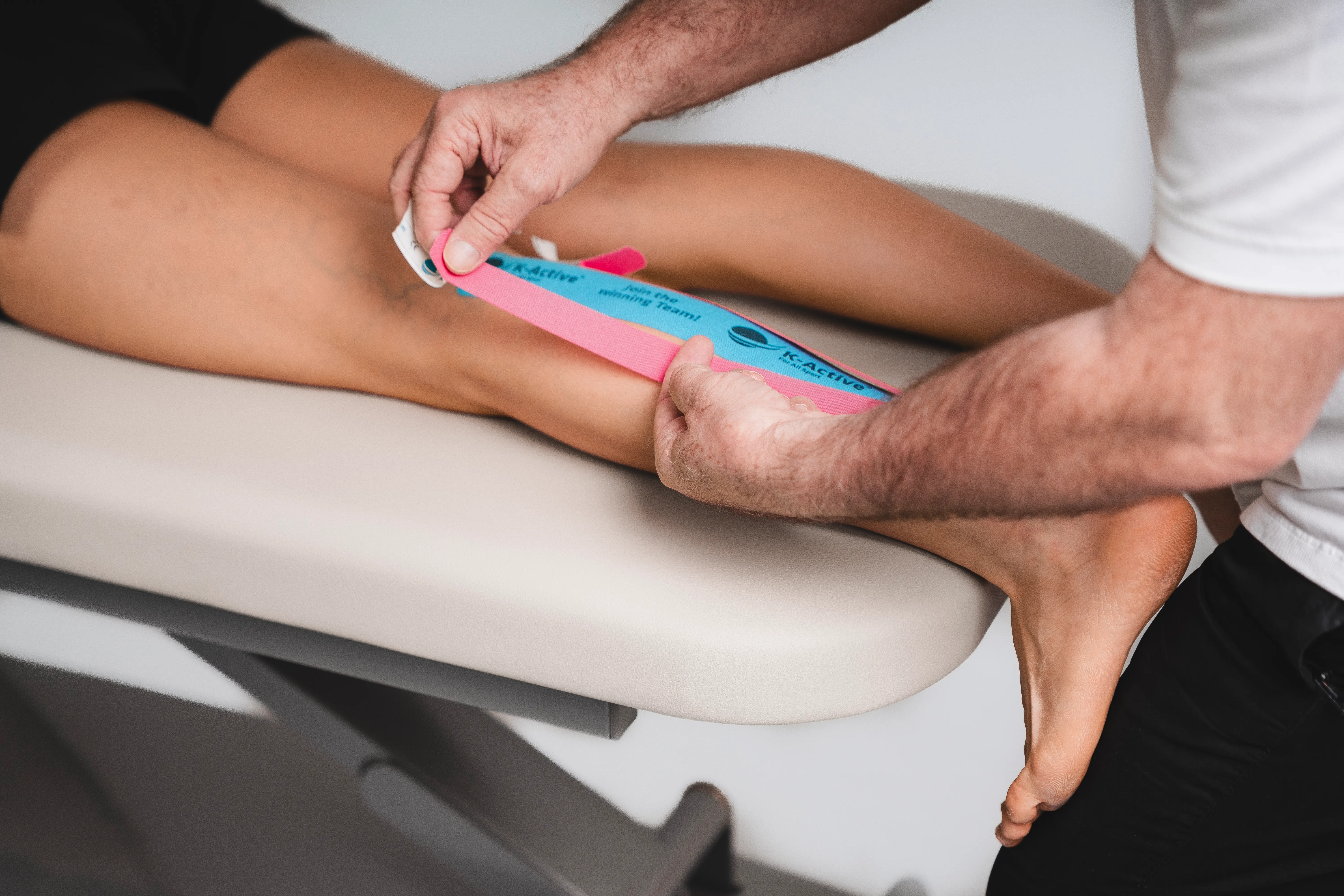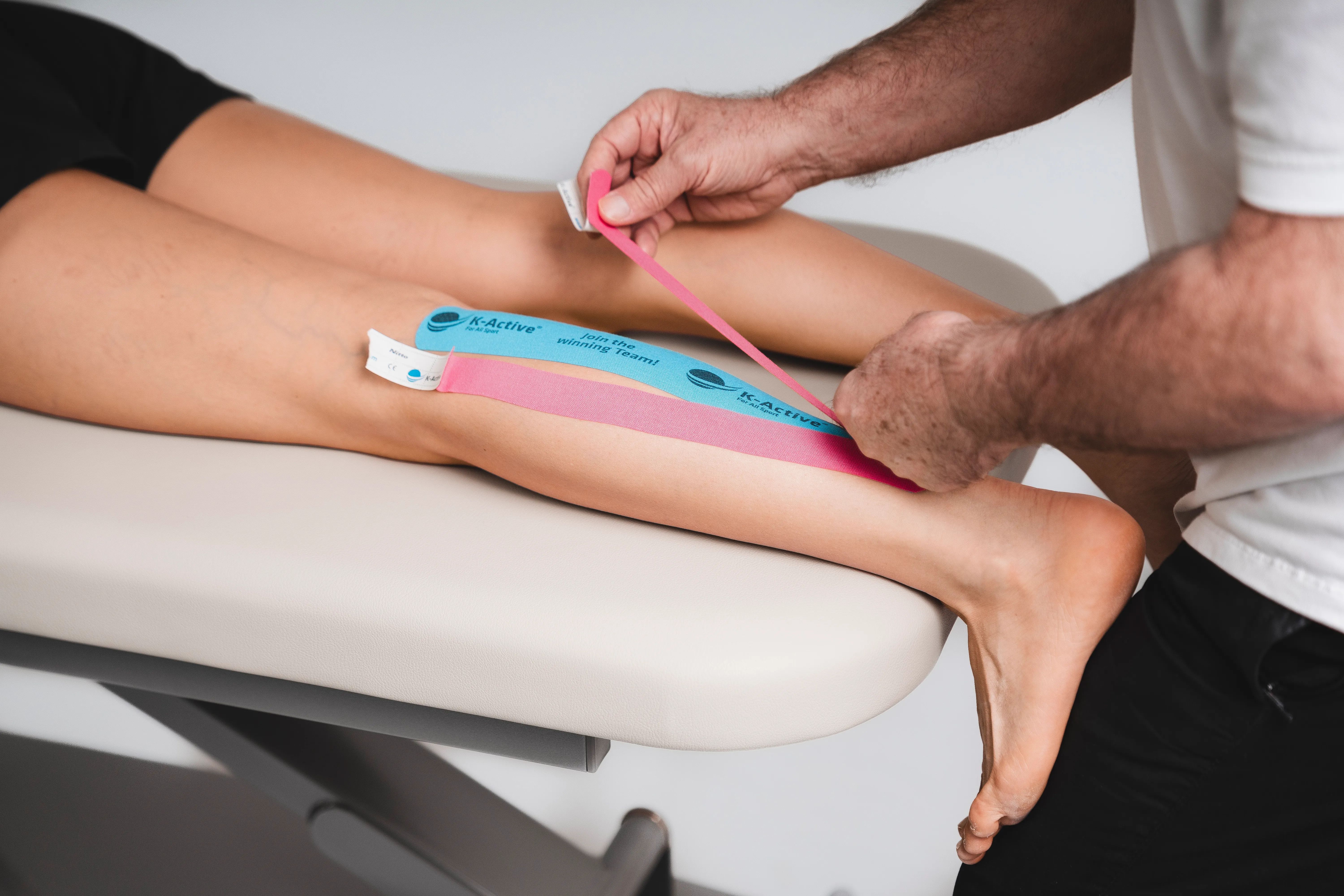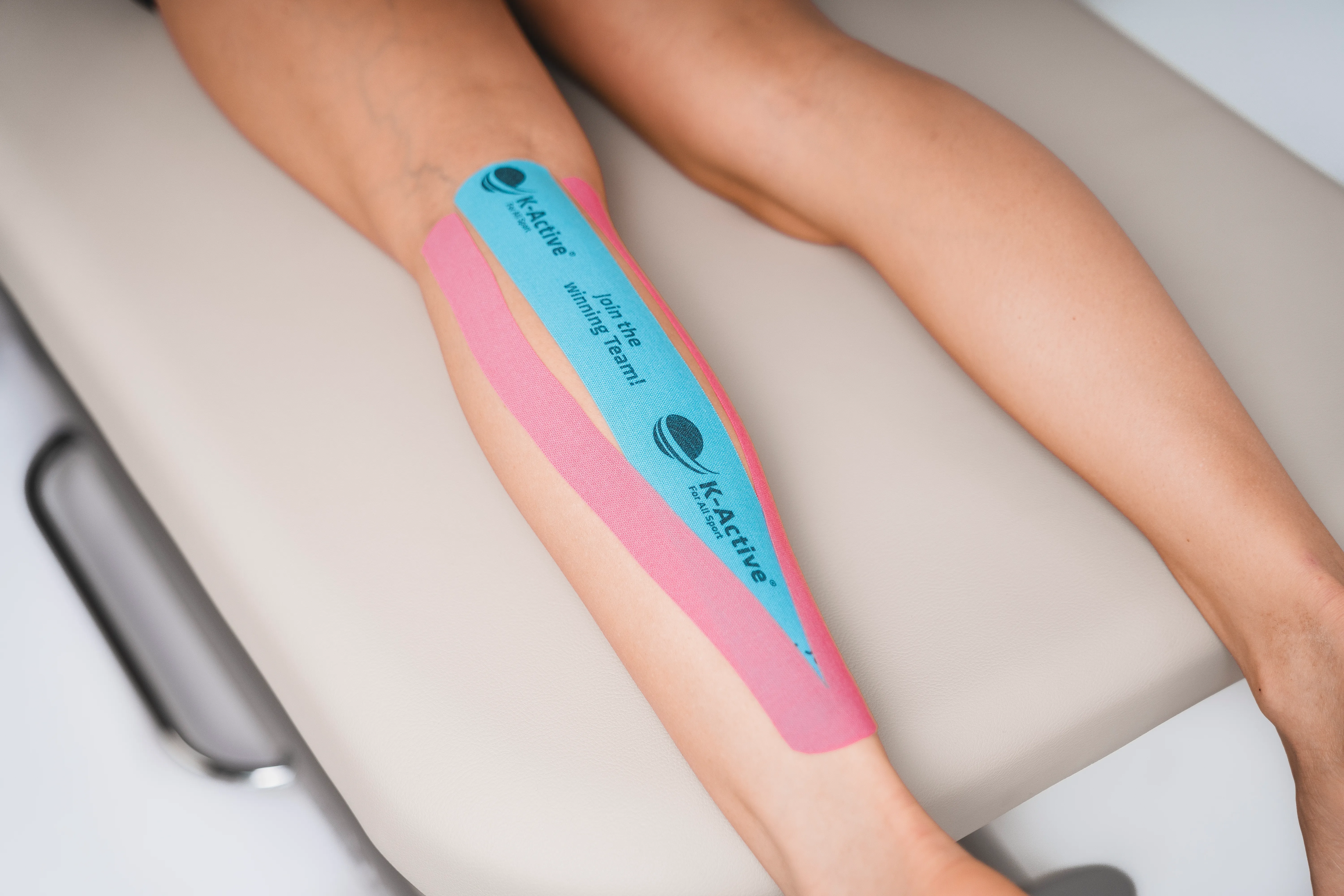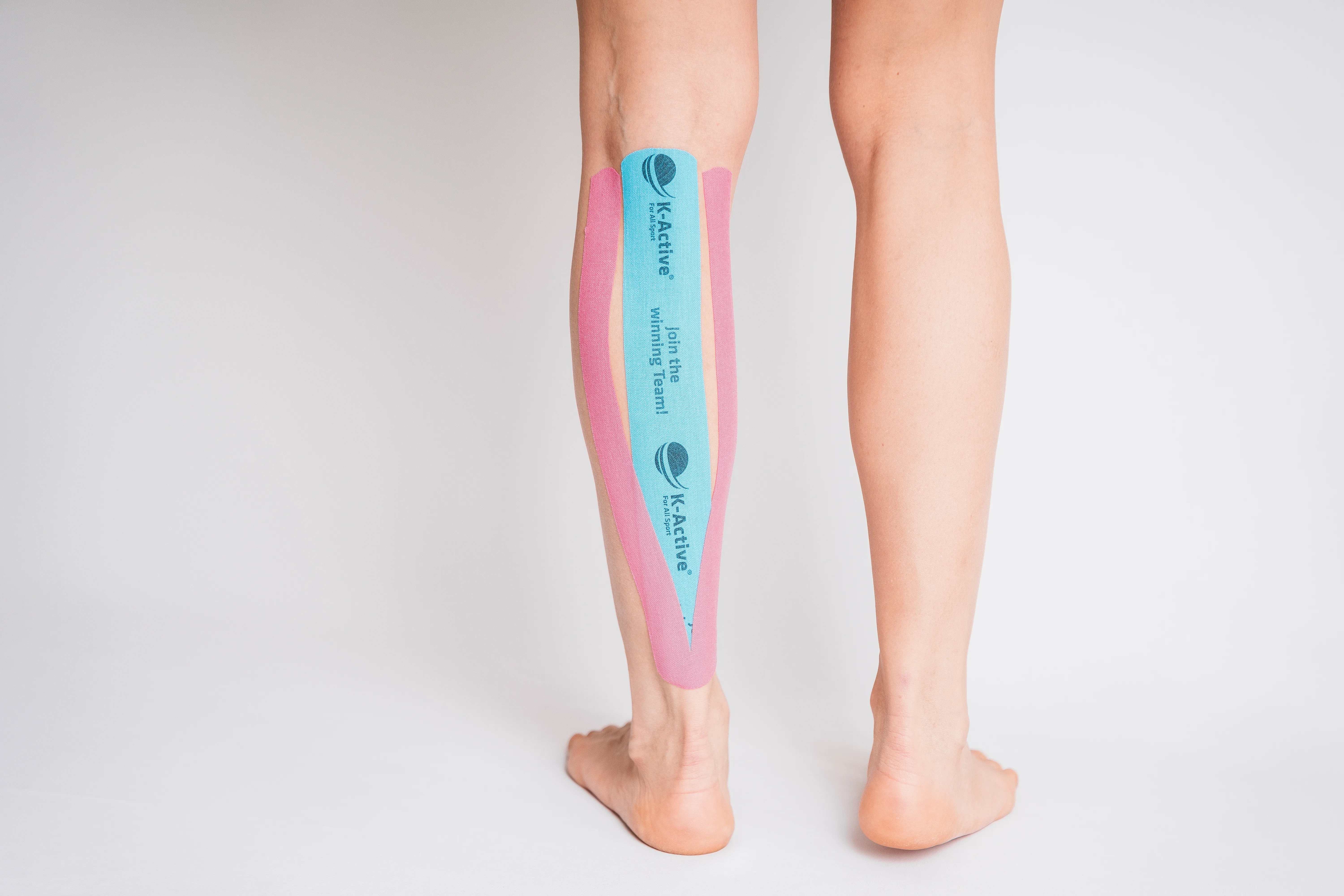
Taping calf
K-Active
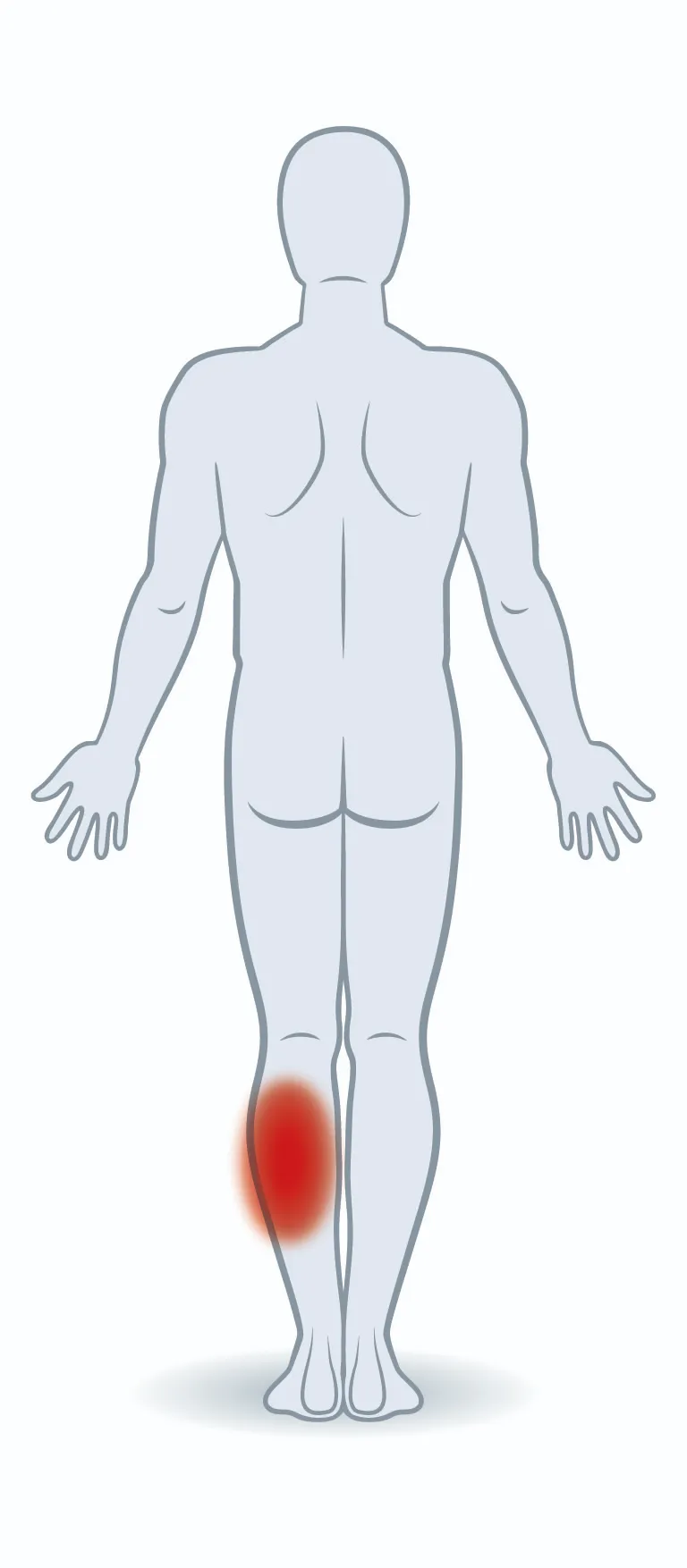
Main area of application
Calf strain
Muscle hardening
Muscle sores
What you need
2 tape strips:
1 x tape (blue) -> about 25 - 30 cm
1 x tape (pink) -> about 20 - 25 cm
Duration of application
Up to 7 days
Information
Taping calf - Tips